Results
Loading...
| java.lang.Object | |
| ↳ | android.media.MediaDrm |
MediaDrm can be used to obtain keys for decrypting protected media streams, in
conjunction with MediaCrypto. The MediaDrm APIs
are designed to support the ISO/IEC 23001-7: Common Encryption standard, but
may also be used to implement other encryption schemes.
Encrypted content is prepared using an encryption server and stored in a content library. The encrypted content is streamed or downloaded from the content library to client devices via content servers. Licenses to view the content are obtained from a License Server.
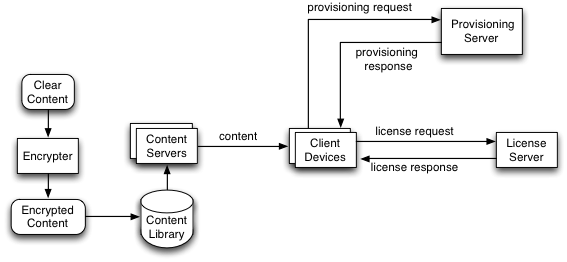
Keys are requested from the license server using a key request. The key response is delivered to the client app, which provides the response to the MediaDrm API.
A Provisioning server may be required to distribute device-unique credentials to the devices.
Enforcing requirements related to the number of devices that may play content simultaneously can be performed either through key renewal or using the secure stop methods.
The following sequence diagram shows the interactions between the objects involved while playing back encrypted content:

The app first constructs MediaExtractor and
MediaCodec objects. It accesses the DRM-scheme-identifying UUID,
typically from metadata in the content, and uses this UUID to construct an instance
of a MediaDrm object that is able to support the DRM scheme required by the content.
Crypto schemes are assigned 16 byte UUIDs. The method isCryptoSchemeSupported(UUID)
can be used to query if a given scheme is supported on the device.
The app calls openSession() to generate a sessionId that will uniquely identify
the session in subsequent interactions. The app next uses the MediaDrm object to
obtain a key request message and send it to the license server, then provide
the server's response to the MediaDrm object.
Once the app has a sessionId, it can construct a MediaCrypto object from the UUID and
sessionId. The MediaCrypto object is registered with the MediaCodec in the
configure(MediaFormat, Surface, MediaCrypto, int) method to enable the codec to decrypt content.
When the app has constructed MediaExtractor,
MediaCodec and MediaCrypto objects,
it proceeds to pull samples from the extractor and queue them into the decoder. For
encrypted content, the samples returned from the extractor remain encrypted, they
are only decrypted when the samples are delivered to the decoder.
Applications should register for informational events in order
to be informed of key state updates during playback or streaming.
Registration for these events is done via a call to
setOnEventListener(MediaDrm.OnEventListener). In order to receive the respective
callback associated with this listener, applications are required to create
MediaDrm objects on a thread with its own Looper running (main UI
thread by default has a Looper running).
| Nested Classes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MediaDrm.CryptoSession | In addition to supporting decryption of DASH Common Encrypted Media, the MediaDrm APIs provide the ability to securely deliver session keys from an operator's session key server to a client device, based on the factory-installed root of trust, and then perform encrypt, decrypt, sign and verify operations with the session key on arbitrary user data. | ||||||||||
| MediaDrm.KeyRequest | Contains the opaque data an app uses to request keys from a license server | ||||||||||
| MediaDrm.OnEventListener | Interface definition for a callback to be invoked when a drm event occurs | ||||||||||
| MediaDrm.ProvisionRequest | Contains the opaque data an app uses to request a certificate from a provisioning server | ||||||||||
| Constants | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| int | EVENT_KEY_EXPIRED | This event type indicates that the licensed usage duration for keys in a session has expired. | |||||||||
| int | EVENT_KEY_REQUIRED | This event type indicates that the app needs to request keys from a license server. | |||||||||
| int | EVENT_PROVISION_REQUIRED | This event type indicates that the app needs to request a certificate from the provisioning server. | |||||||||
| int | EVENT_VENDOR_DEFINED | This event may indicate some specific vendor-defined condition, see your DRM provider documentation for details | |||||||||
| int | KEY_TYPE_OFFLINE | This key request type specifies that the keys will be for offline use, they will be saved to the device for use when the device is not connected to a network. | |||||||||
| int | KEY_TYPE_RELEASE | This key request type specifies that previously saved offline keys should be released. | |||||||||
| int | KEY_TYPE_STREAMING | This key request type species that the keys will be for online use, they will not be saved to the device for subsequent use when the device is not connected to a network. | |||||||||
| String | PROPERTY_ALGORITHMS | String property name: a comma-separated list of cipher and mac algorithms supported by CryptoSession. | |||||||||
| String | PROPERTY_DESCRIPTION | String property name: describes the DRM engine plugin | |||||||||
| String | PROPERTY_DEVICE_UNIQUE_ID | Byte array property name: the device unique identifier is established during device provisioning and provides a means of uniquely identifying each device. | |||||||||
| String | PROPERTY_VENDOR | String property name: identifies the maker of the DRM engine plugin | |||||||||
| String | PROPERTY_VERSION | String property name: identifies the version of the DRM engine plugin | |||||||||
| Public Constructors | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Instantiate a MediaDrm object
| |||||||||||
| Public Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Close a session on the MediaDrm object that was previously opened
with
openSession(). | |||||||||||
Obtain a CryptoSession object which can be used to encrypt, decrypt,
sign and verify messages or data using the session keys established
for the session using methods
getKeyRequest(byte[], byte[], String, int, HashMap and
provideKeyResponse(byte[], byte[]) using a session key server. | |||||||||||
A key request/response exchange occurs between the app and a license server
to obtain or release keys used to decrypt encrypted content.
| |||||||||||
Read a DRM engine plugin byte array property value, given the property name string.
| |||||||||||
Read a DRM engine plugin String property value, given the property name string.
| |||||||||||
A provision request/response exchange occurs between the app and a provisioning
server to retrieve a device certificate.
| |||||||||||
A means of enforcing limits on the number of concurrent streams per subscriber
across devices is provided via SecureStop.
| |||||||||||
Query if the given scheme identified by its UUID is supported on
this device, and whether the drm plugin is able to handle the
media container format specified by mimeType.
| |||||||||||
Query if the given scheme identified by its UUID is supported on
this device.
| |||||||||||
Open a new session with the MediaDrm object.
| |||||||||||
A key response is received from the license server by the app, then it is
provided to the DRM engine plugin using provideKeyResponse.
| |||||||||||
After a provision response is received by the app, it is provided to the DRM
engine plugin using this method.
| |||||||||||
Request an informative description of the key status for the session.
| |||||||||||
Process the SecureStop server response message ssRelease.
| |||||||||||
Remove the current keys from a session.
| |||||||||||
Restore persisted offline keys into a new session.
| |||||||||||
Register a callback to be invoked when an event occurs
| |||||||||||
Set a DRM engine plugin byte array property value.
| |||||||||||
Set a DRM engine plugin String property value.
| |||||||||||
| Protected Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Invoked when the garbage collector has detected that this instance is no longer reachable.
| |||||||||||
|
[Expand]
Inherited Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 From class
java.lang.Object
From class
java.lang.Object
| |||||||||||
This event type indicates that the licensed usage duration for keys in a session has expired. The keys are no longer valid.
This event type indicates that the app needs to request keys from a license
server. The request message data is obtained using getKeyRequest(byte[], byte[], String, int, HashMap.
This event type indicates that the app needs to request a certificate from
the provisioning server. The request message data is obtained using
getProvisionRequest()
This event may indicate some specific vendor-defined condition, see your DRM provider documentation for details
This key request type specifies that the keys will be for offline use, they will be saved to the device for use when the device is not connected to a network.
This key request type specifies that previously saved offline keys should be released.
This key request type species that the keys will be for online use, they will not be saved to the device for subsequent use when the device is not connected to a network.
String property name: a comma-separated list of cipher and mac algorithms supported by CryptoSession. The list may be empty if the DRM engine plugin does not support CryptoSession operations.
String property name: describes the DRM engine plugin
Byte array property name: the device unique identifier is established during device provisioning and provides a means of uniquely identifying each device.
String property name: identifies the maker of the DRM engine plugin
String property name: identifies the version of the DRM engine plugin
Instantiate a MediaDrm object
| uuid | The UUID of the crypto scheme. |
|---|
| UnsupportedSchemeException | if the device does not support the specified scheme UUID |
|---|
Close a session on the MediaDrm object that was previously opened
with openSession().
Obtain a CryptoSession object which can be used to encrypt, decrypt,
sign and verify messages or data using the session keys established
for the session using methods getKeyRequest(byte[], byte[], String, int, HashMap and
provideKeyResponse(byte[], byte[]) using a session key server.
| sessionId | the session ID for the session containing keys to be used for encrypt, decrypt, sign and/or verify |
|---|---|
| cipherAlgorithm | the algorithm to use for encryption and decryption ciphers. The algorithm string conforms to JCA Standard Names for Cipher Transforms and is case insensitive. For example "AES/CBC/NoPadding". |
| macAlgorithm | the algorithm to use for sign and verify
The algorithm string conforms to JCA Standard Names for Mac
Algorithms and is case insensitive. For example "HmacSHA256".
The list of supported algorithms for a DRM engine plugin can be obtained
using the method |
A key request/response exchange occurs between the app and a license server to obtain or release keys used to decrypt encrypted content.
getKeyRequest() is used to obtain an opaque key request byte array that is delivered to the license server. The opaque key request byte array is returned in KeyRequest.data. The recommended URL to deliver the key request to is returned in KeyRequest.defaultUrl.
After the app has received the key request response from the server,
it should deliver to the response to the DRM engine plugin using the method
provideKeyResponse(byte[], byte[]).
| scope | may be a sessionId or a keySetId, depending on the specified keyType. When the keyType is KEY_TYPE_STREAMING or KEY_TYPE_OFFLINE, scope should be set to the sessionId the keys will be provided to. When the keyType is KEY_TYPE_RELEASE, scope should be set to the keySetId of the keys being released. Releasing keys from a device invalidates them for all sessions. |
|---|---|
| init | container-specific data, its meaning is interpreted based on the mime type provided in the mimeType parameter. It could contain, for example, the content ID, key ID or other data obtained from the content metadata that is required in generating the key request. init may be null when keyType is KEY_TYPE_RELEASE. |
| mimeType | identifies the mime type of the content |
| keyType | specifes the type of the request. The request may be to acquire keys for streaming or offline content, or to release previously acquired keys, which are identified by a keySetId. |
| optionalParameters | are included in the key request message to allow a client application to provide additional message parameters to the server. |
| NotProvisionedException | if reprovisioning is needed, due to a problem with the certifcate |
|---|
Read a DRM engine plugin byte array property value, given the property name string.
Standard fields names are PROPERTY_DEVICE_UNIQUE_ID
Read a DRM engine plugin String property value, given the property name string.
Standard fields names are:
PROPERTY_VENDOR, PROPERTY_VERSION,
PROPERTY_DESCRIPTION, PROPERTY_ALGORITHMS
A provision request/response exchange occurs between the app and a provisioning server to retrieve a device certificate. If provisionining is required, the EVENT_PROVISION_REQUIRED event will be sent to the event handler. getProvisionRequest is used to obtain the opaque provision request byte array that should be delivered to the provisioning server. The provision request byte array is returned in ProvisionRequest.data. The recommended URL to deliver the provision request to is returned in ProvisionRequest.defaultUrl.
A means of enforcing limits on the number of concurrent streams per subscriber across devices is provided via SecureStop. This is achieved by securely monitoring the lifetime of sessions.
Information from the server related to the current playback session is written to persistent storage on the device when each MediaCrypto object is created.
In the normal case, playback will be completed, the session destroyed and the Secure Stops will be queried. The app queries secure stops and forwards the secure stop message to the server which verifies the signature and notifies the server side database that the session destruction has been confirmed. The persisted record on the client is only removed after positive confirmation that the server received the message using releaseSecureStops().
Query if the given scheme identified by its UUID is supported on this device, and whether the drm plugin is able to handle the media container format specified by mimeType.
| uuid | The UUID of the crypto scheme. |
|---|---|
| mimeType | The MIME type of the media container, e.g. "video/mp4" or "video/webm" |
Query if the given scheme identified by its UUID is supported on this device.
| uuid | The UUID of the crypto scheme. |
|---|
Open a new session with the MediaDrm object. A session ID is returned.
| NotProvisionedException | if provisioning is needed |
|---|---|
| ResourceBusyException | if required resources are in use |
A key response is received from the license server by the app, then it is
provided to the DRM engine plugin using provideKeyResponse. When the
response is for an offline key request, a keySetId is returned that can be
used to later restore the keys to a new session with the method
restoreKeys(byte[], byte[]).
When the response is for a streaming or release request, null is returned.
| scope | may be a sessionId or keySetId depending on the type of the response. Scope should be set to the sessionId when the response is for either streaming or offline key requests. Scope should be set to the keySetId when the response is for a release request. |
|---|---|
| response | the byte array response from the server |
| NotProvisionedException | if the response indicates that reprovisioning is required |
|---|---|
| DeniedByServerException | if the response indicates that the server rejected the request |
| ResourceBusyException | if required resources are in use |
After a provision response is received by the app, it is provided to the DRM engine plugin using this method.
| response | the opaque provisioning response byte array to provide to the DRM engine plugin. |
|---|
| DeniedByServerException | if the response indicates that the server rejected the request |
|---|
Request an informative description of the key status for the session. The status is in the form of {name, value} pairs. Since DRM license policies vary by vendor, the specific status field names are determined by each DRM vendor. Refer to your DRM provider documentation for definitions of the field names for a particular DRM engine plugin.
| sessionId | the session ID for the DRM session |
|---|
Process the SecureStop server response message ssRelease. After authenticating the message, remove the SecureStops identified in the response.
| ssRelease | the server response indicating which secure stops to release |
|---|
Remove the current keys from a session.
| sessionId | the session ID for the DRM session |
|---|
Restore persisted offline keys into a new session. keySetId identifies the
keys to load, obtained from a prior call to provideKeyResponse(byte[], byte[]).
| sessionId | the session ID for the DRM session |
|---|---|
| keySetId | identifies the saved key set to restore |
Register a callback to be invoked when an event occurs
| listener | the callback that will be run |
|---|
Set a DRM engine plugin byte array property value.
Set a DRM engine plugin String property value.
Invoked when the garbage collector has detected that this instance is no longer reachable. The default implementation does nothing, but this method can be overridden to free resources.
Note that objects that override finalize are significantly more expensive than
objects that don't. Finalizers may be run a long time after the object is no longer
reachable, depending on memory pressure, so it's a bad idea to rely on them for cleanup.
Note also that finalizers are run on a single VM-wide finalizer thread,
so doing blocking work in a finalizer is a bad idea. A finalizer is usually only necessary
for a class that has a native peer and needs to call a native method to destroy that peer.
Even then, it's better to provide an explicit close method (and implement
Closeable), and insist that callers manually dispose of instances. This
works well for something like files, but less well for something like a BigInteger
where typical calling code would have to deal with lots of temporaries. Unfortunately,
code that creates lots of temporaries is the worst kind of code from the point of view of
the single finalizer thread.
If you must use finalizers, consider at least providing your own
ReferenceQueue and having your own thread process that queue.
Unlike constructors, finalizers are not automatically chained. You are responsible for
calling super.finalize() yourself.
Uncaught exceptions thrown by finalizers are ignored and do not terminate the finalizer thread. See Effective Java Item 7, "Avoid finalizers" for more.