Topics
Android supports a variety of USB peripherals and Android USB accessories (hardware that implements the Android accessory protocol) through two modes: USB accessory and USB host. In USB accessory mode, the external USB hardware act as the USB hosts. Examples of accessories might include robotics controllers; docking stations; diagnostic and musical equipment; kiosks; card readers; and much more. This gives Android-powered devices that do not have host capabilities the ability to interact with USB hardware. Android USB accessories must be designed to work with Android-powered devices and must adhere to the Android accessory communication protocol. In USB host mode, the Android-powered device acts as the host. Examples of devices include digital cameras, keyboards, mice, and game controllers. USB devices that are designed for a wide range of applications and environments can still interact with Android applications that can correctly communicate with the device.
Figure 1 shows the differences between the two modes. When the Android-powered device is in host mode, it acts as the USB host and powers the bus. When the Android-powered device is in USB accessory mode, the connected USB hardware (an Android USB accessory in this case) acts as the host and powers the bus.
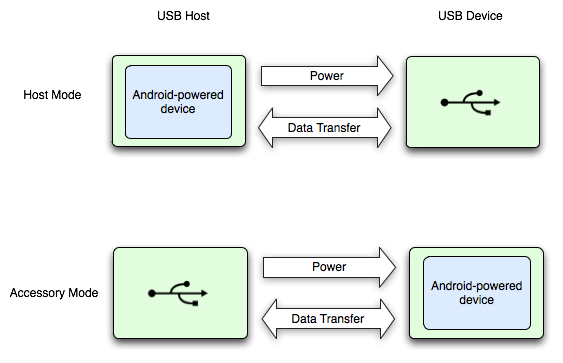
Figure 1. USB Host and Accessory Modes
USB accessory and host modes are directly supported in Android 3.1 (API level 12) or newer platforms. USB accessory mode is also backported to Android 2.3.4 (API level 10) as an add-on library to support a broader range of devices. Device manufacturers can choose whether or not to include the add-on library on the device's system image.
Note: Support for USB host and accessory modes are ultimately dependant on the device's hardware, regardless of platform level. You can filter for devices that support USB host and accessory through a <uses-feature> element. See the USB accessory and host documentation for more details.
Debugging considerations
When debugging applications that use USB accessory or host features, you most likely will have
USB hardware connected to your Android-powered device. This will prevent you from having an
adb connection to the Android-powered device via USB. You can still access
adb over a network connection. To enable adb over a network
connection:
- Connect the Android-powered device via USB to your computer.
- From your SDK
platform-tools/directory, enteradb tcpip 5555at the command prompt. - Enter
adb connect <device-ip-address>:5555You should now be connected to the Android-powered device and can issue the usualadbcommands likeadb logcat. - To set your device to listen on USB, enter
adb usb.